When it comes to marketing strategy, the Ansoff Matrix emerges as a pivotal tool, essential for business growth and market expansion.
Often referred to as the product-market expansion grid, the Ansoff Matrix provides a roadmap for businesses seeking to explore new markets or expand their existing market segments.
Created by H. Igor Ansoff and first published in the Harvard Business Review, this matrix has become a cornerstone in the strategic planning process for marketing leaders and business managers alike looking to emerge in new or existing markets.
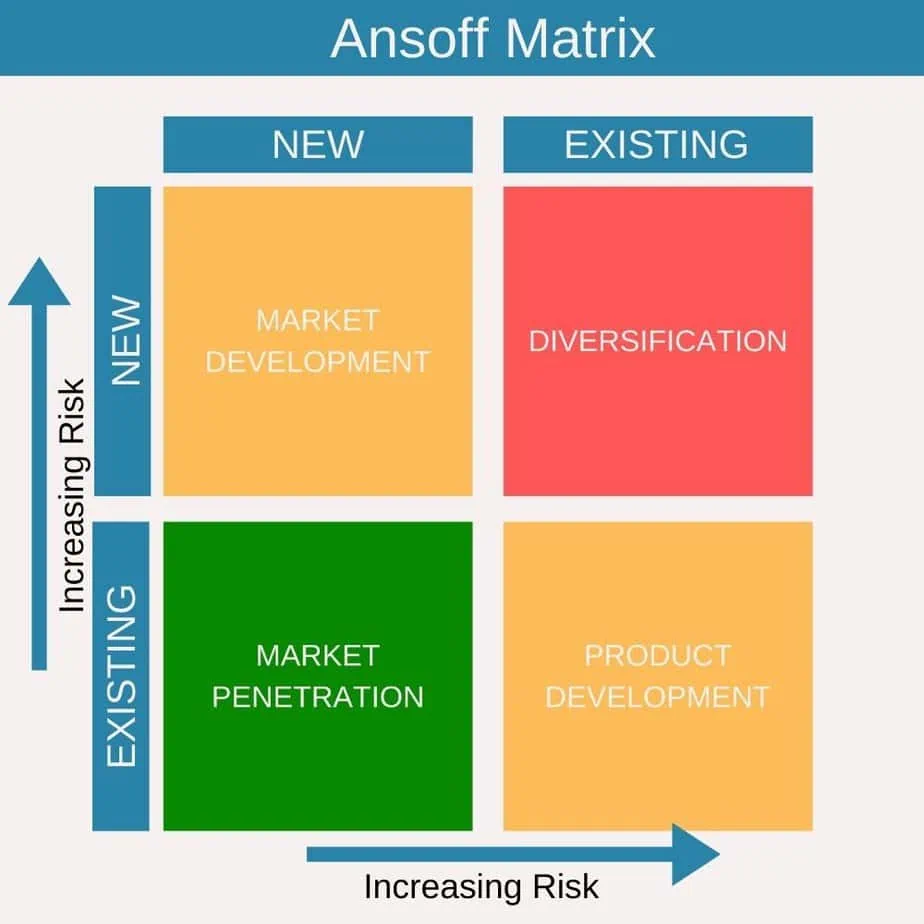
It lays out four different growth strategies: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification, each offering a unique pathway to business expansion.
Understanding the Ansoff Matrix: The Basics
The essence of the Ansoff Matrix lies in its simplicity and clarity in categorizing growth strategies. The matrix forms a grid with two dimensions: products and markets.
Each dimension is divided into ‘new’ and ‘existing,’ creating four distinct quadrants. These quadrants guide businesses in strategizing their growth pathways, whether through existing offerings or venturing into uncharted territories.
Market Penetration
This strategy focuses on increasing market share within existing market segments using existing products. It’s about getting current customers to buy more or attracting customers from competitors. It often involves intensified marketing efforts, promotional tactics, and possibly even entering new sales channels within the same market.
Market Development
Here, the goal is to enter new markets or target new customer segments with existing products. This could mean expanding into foreign markets, targeting different customer segments (like industrial buyers), or using different distribution processes to reach a new market segment.
It requires significant market research and may involve tweaking existing offerings to suit the new audience.
Product Development
This quadrant is about introducing new offerings or features to the existing customer base. It involves innovation and development of new products or enhancements to meet the evolving needs of the current market.
This could range from adding new features to existing products to developing entirely new product lines.
Diversification Strategy
The most ambitious of the four strategies, diversification involves introducing new products to new markets.
It can be related diversification (new products that are somewhat related to the existing business) or unrelated diversification (venturing into entirely different industries). This strategy carries the highest risk but also offers potential new revenue opportunities.
Diving Deeper: Each Quadrant of the Ansoff Matrix
Each quadrant of the Ansoff Matrix requires a unique approach, considering the varying levels of risk and investment:
Market Penetration Strategy
Typically the safest of the four strategies, it involves focusing on increasing sales of existing products in the existing markets.
Tactics might include aggressive pricing strategies, marketing campaigns aimed at the existing customer segments, or exploring new marketing channels. The main advantage here is the familiarity with the market and customer base.
Market Development Strategy
This strategy demands a deep understanding of the new market, including customer preferences, local market conditions, and competitive landscape.
For instance, international expansion or targeting different market segments like consumer versus industrial buyers requires adapting marketing efforts to suit these new audiences.
Product Development Strategy
It revolves around innovation and understanding customer needs. The management team needs to assess if the existing customer base will appreciate and accept the new offerings. This strategy often involves research and development, and may require a revamp of the production process.
Diversification Strategy
As it involves both new products and new markets, the risk increases significantly. Here, businesses must conduct robust assessments of both the product’s potential and the new market’s dynamics. Diversification can range from developing a white label product for a different industry to creating a completely new product line for a foreign market.
Each strategy in the Ansoff Matrix offers different growth opportunities and challenges. A business’s choice among these strategies often depends on its risk appetite, market conditions, and the strengths of its existing products and market segments.
Applying the Ansoff Matrix in Business
The application of the Ansoff Matrix in a business context is a strategic exercise that enables companies to chart their growth trajectories with a clearer vision.
Utilizing this matrix involves a thorough examination of a company’s current market position, its product range, and potential avenues for expansion.
The process starts with an in-depth analysis of the current market segments and customer base, evaluating how well existing products are performing.
From there, businesses can explore various pathways for growth, each aligned with one of the four strategies outlined in the matrix.
For instance, a business looking to expand might use market research to explore new customer segments or foreign markets. This exploration is crucial for market development, where understanding the nuances of different markets can make or break the success of the expansion.
Similarly, product development requires a keen insight into the existing customer base’s needs and preferences, ensuring that any new offerings align with their expectations.
Diversification, being the most complex, requires an assessment of both new product viability and new market potential, often necessitating significant investment in both market research and product development.
Real-World Examples of the Ansoff Matrix in Action
The practical application of the Ansoff Matrix across various industries provides insights into its versatility and effectiveness:
- Technology Sector: A technology company might use the Ansoff Matrix to diversify its product range. Recognizing the saturation in its current market, the company could innovate new product lines, venturing into different technological domains, or even different market segments like industrial buyers.
- Retail Industry: A retail business could implement a market development strategy by opening new stores in foreign markets or developing an online sales channel to tap into a broader customer base. This expansion allows the company to reach new market segments that were previously untapped.
- Consumer Goods: A consumer goods company might focus on product development, adding new features to existing products, or creating entirely new offerings to maintain its competitive edge in the existing market. This approach keeps the product range fresh and appealing to the existing customer base.
Advantages and Limitations of the Ansoff Matrix
While the Ansoff Matrix is a valuable tool for strategic planning, it comes with its own set of advantages and limitations:
- Advantages:
The matrix offers a clear and straightforward framework for thinking about growth. It simplifies the decision-making process by categorizing growth strategies into four distinct quadrants.
It encourages companies to diversify their risk by considering different growth strategies. This can be particularly valuable in dynamic markets where relying on a single strategy might be risky.
- Limitations:
One of the primary limitations is that the matrix doesn’t take into account the external environment factors that could impact the success of each strategy, such as competition and market changes.
The matrix also oversimplifies the growth strategies and doesn’t account for the complexities and nuances involved in implementing each strategy.
Despite these limitations, the Ansoff Matrix remains a popular tool among business leaders and marketing strategists for its ability to provide a structured and focused approach to growth.
In the next sections, we will explore the matrix’s relevance in today’s business world and strategic considerations for its successful implementation.
The Ansoff Matrix in the Modern Business Context
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the Ansoff Matrix continues to hold significant relevance. Its enduring appeal lies in its adaptability to various market scenarios and its ability to offer strategic direction amidst the complexities of modern business environments.
- Relevance in Today’s Dynamic Market Environment: The matrix’s straightforward approach to categorizing growth strategies makes it an invaluable tool for businesses navigating through fast-paced market changes. In an era where market dynamics shift quickly, the Ansoff Matrix provides a structured framework for businesses to reassess their strategies and explore new growth opportunities, whether through tapping into new markets or innovating their product offerings.
- Evolving the Matrix for Contemporary Use: Modern businesses often adapt the Ansoff Matrix to include more nuanced considerations of the digital landscape, such as online customer segments or digital marketing channels. The flexibility of the matrix allows it to be used in conjunction with other strategic tools, such as SWOT analysis or PESTLE analysis, for more robust assessments of business opportunities and challenges.
Strategic Considerations When Using the Ansoff Matrix
When employing the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic tool, businesses must consider several key factors to ensure its effective implementation:
- Understanding the Target Audience: Whether pursuing market penetration or market development strategies, a deep understanding of the target audience is crucial. Businesses should conduct thorough market research to understand the needs and preferences of both existing and potential customer segments.
- Assessing Risk Appetite: Each quadrant of the Ansoff Matrix comes with varying levels of risk. For instance, diversification strategies typically involve higher risk compared to market penetration strategies. Businesses need to assess their risk tolerance levels and ensure that their strategic choices align with their overall risk management approach.
- Resource Allocation: Effective use of the Ansoff Matrix requires careful consideration of resource allocation. Businesses should evaluate their capabilities and resources to determine whether they can support the chosen growth strategy, whether it’s venturing into foreign markets or investing in the development of new products.
Conclusion
The Ansoff Matrix remains a fundamental tool in strategic planning, offering a clear and practical approach to exploring growth strategies.
From market penetration to diversification, it guides businesses in aligning their strategies with market conditions and internal capabilities.
While it may not encompass all the complexities of the modern business environment, its simplicity and adaptability make it a valuable tool for businesses looking to navigate growth and expansion.
As businesses continue to evolve in a dynamic marketplace, the Ansoff Matrix serves as a reliable roadmap, aiding business leaders and marketing strategists in making informed decisions for the future.








0 Comments